 Index
Index

Arthritis is a painful condition of the joints that often leads to disability. The word "arthritis" is derived from the Greek roots arthro- meaning joint and the suffix -itis for inflammation. The plural form is "arthritides". Some of the most common forms of arthritis are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout.
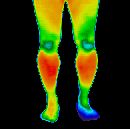
What is Gout?
Gout occurs when too much uric acid builds up in the blood and uric acid
crystals precipitate in the cooler parts of the body such as the joints of the hands or feet.
High levels of uric acid may also build up as lumps under the skin called tophi,
or as kidney stones.
Uric Acid is a waste product of the oxidation of purines which are constituents of nucleic acids
such as DNA. Uric acid is normally excreted in the urine to maintain a concentration
of uric acid in the blood of approximately 4 mg/dL. When the concentration exceeds 7 mg/dL,
crystals of monosodium urate start to form in the tissues. This condition is known as hyperuricemia.
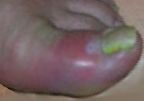
What are the symptoms of Gout?
The symptoms of gout are redness of a joint, accompanied by inflammation,
stiffness, and intense pain. Many people experience their first gout attack in the
big toe, but other joints such as the ankles, wrists, fingers, or elbows may be affected.
The pain may be so severe that even the pressure of bed sheets may be unbearable.
A gout attack can be brought on by alcohol, or foods high in purines such as shellfish,
caviar, sardines, anchovies, meats, or organ meats that are commonly used in sausages.
A study over a 12-year period of 47,000 adult men revealed that those who ate the most red meat
or seafood increased their risk of gout by as much as 50%.[6]
Many gout attacks get better within a few days, even without treatment, and they
may not recur for many months or years.
How is Gout Diagnosed?
Gout is diagnosed based on family history, specific symptoms, and laboratory tests.
Diagnosis of gout is confirmed by the determination of high levels of uric
acid in the blood, monosodium urate crystals in the fluid of an inflamed joint, more than one
attack of acute arthritis, and the involvement of only one joint such as the toe, ankle, or knee.
How is Gout treated?
Because gout episodes are so painful, patients demand some kind of gout treatment, even though
the treatments for gout are not very effective and have undesirable side effects.
The most common treatments include the administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
such as ibuprofen, indomethacin and naproxen. Aspirin is not used because it aggravates hyperuricemia
by increasing uric acid retention.[17]
These medications can cause stomach pain, bleeding and ulcers,
and beyond a certain dosage, they do not provide additional relief.
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are prescribed for severe cases of gout. Although these steroids can provide relief, they also have serious side effects, including thinning bones, poor wound healing, and a weakened immune system. Cortisone injections into an affected joint are generally limited to no more than three per year because of the side effects.
Allopurinol, probenecid, and colchicine are sometimes prescribed in daily doses to reduce the risk or lessen the severity of future episodes. Allopurinol blocks the formation of uric acid, probenecid decreases the frequency of attacks of gout by increasing the kidney's excretion of uric acid, and colchicine may relieve swelling and help prevent the frequency of gout attacks. These drugs speed the elimination of uric acid from the body, and they also slow down the rate at which it is produced, but they may cause nausea or skin rashes as side effects.
Some new drugs for the treatment of gout include febuxostat (Uloric) which was introduced in 2009 for the chronic management of hyperuricemia in patients with gout. It is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor that works by decreasing the amount of uric acid made in the body. Febuxostat must be taken daily and it may take several months before it begins to prevent gout attacks. As a side effect, febuxostat may cause increased levels of liver enzymes in the blood that may be a sign of liver damage. Pegloticase (Krystexxa) is a urate oxidase enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of uric acid to allantoin which is five to ten times more soluble than uric acid. In 2010, the FDA approved pegloticase for treatment of gout patients who cannot tolerate or do not respond to conventional therapy. Peglioticase is administered every two weeks by intravenous infusion. Nausea, vomiting and allergic reactions have been reported as side effects.
Along with specifically prescribed medications, patients are advised to drink plenty of water and avoid alcoholic beverages and purine-rich foods such as fish roes, herring, organ meats, legumes, and meats.
Is there a Gout Cure?
Learning about the chemical and physical properties of uric acid and purines can provide
a scientific foundation for relieving gout symptoms and for avoiding its occurrence.
An understanding of the chemical structure of purines
and their origin makes it possible to avoid sources of purines in the diet.
The level of uric acid in the body may also be reduced by drinking plenty of water to increase
the frequency of urination. However, learning how the solubility of uric acid is affected by
temperature and by the acidity of body fluids can be used to formulate some possible home therapies.

What are purines?
Purine is the chemical name of a 6-atom ring fused to a 5-atom ring known as
imidazo[4,5-d]pyrimidine. Compounds containing this substructure are generically called "purines".
The purine structure is present in uric acid, as well as in
caffeine, Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA), Ribonucleic Acid (RNA),
and other important biomolecules such
as ATP, GTP, cyclic AMP, NADH, and coenzyme A.
The main source of dietary purines is the DNA and RNA in the cells of the animal and vegetable foods that we eat.
DNA and RNA are called nucleic acids because they reside in the nucleus of the cells.
Their function is to encode genetic information as
long chains of the four bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine.
Uric acid is produced from the oxidation of adenine and guanine in these nucleic acids.



Adenine and guanine are components of nucleic acids, but not of the amino acids that form proteins. The nitrogen in proteins is excreted as urea which is formed in the liver through the action of a system of carrier molecules and enzymes that combine two molecules of ammonia with one molecule of carbon dioxide (the Urea Cycle).

Foods without purines
Foods that do not have cell nuclei are generally purine free.
Some purine-free foods are:


These foods do not have purines because they do not have cell nuclei. The yolk of an egg contains the nucleic acids, but the egg white is pure protein without purines. Milk contains no purines because it consists of fats, casein and whey proteins, but no cell nuclei. Fermented milk products, such as yogurt and aged cheeses, have purines from the nucleic acids of the bacterial cells that proliferate during fermentation. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine confirms that a higher level of consumption of dairy products has been associated with a decreased risk of gout and that moderate intake of purine-rich vegetables or protein is not associated with an increased risk of gout.[6]
To reduce purines, a gout diet should use egg whites and milk products as sources of protein and eliminate or reduce substantially meats and seafood. The eggs may be hard-boiled before the yolks are removed, or the whites may be separated for making omelettes, as illustrated above. Milk, cottage cheese, mozzarella cheese, and whey protein can be used in a variety of recipes such as fruit smoothies, custards, chef salads, and other dishes that can be delicious and low in purines.
Effect of weight-loss diets
Purines cannot be avoided entirely because they are released in the body
as the result of recycling dead cells. During a gout attack,
it is prudent to avoid excessive exercise and long periods of starvation or caloric restriction
that would accelerate the breakdown of body tissues.
Crash diets for extremely obese patients are inappropriate because
ketosis
raises urate concentration and can cause an acute attack.[8]
Dr. George Nuki, professor of rheumatology at the University of Edinburgh in Scotland, has been quoted
as saying that there is anecdotal evidence that going on an Atkins diet
has exacerbated the problem and precipitated attacks for people with a previous history of gout.
However, there have been no controlled studies that indicate that any particular weight-loss plan
can cause the painful condition.
Gout is more common in overweight people and the risk of gout attacks increases with higher body weights. So, a gradual loss of weight may be beneficial for overweight people who have high levels of uric acid, even though dieting has the risk of triggering a gout attack. A pilot study of 13 non-diabetic men who had had at least two gouty attacks during the four months before the study found lower levels of serum uric acid after 16 weeks of administering a 1600-calorie diet consisting of 30% protein, 30% fat, and 40% carbohydrate. The average body mass index (BMI) decreased from 30.5 to 27.8, and the weight loss was accompanied by a decrease in the frequency and severity of gout attacks.[11]
Avoid alcoholic beverages, niacin supplements, and sugary soft drinks
Why do alcoholic beverages trigger episodes of gout? One reason is that uric acid is
insoluble in alcohol.[1] As the alcohol content of the blood increases, the blood is not able
to dissolve as much uric acid, and the excess crystalizes.
Gout problems are compounded because acute and chronic alcohol consumption impair the function of the kidneys.
Alcohol increases purine
catabolism
in the liver and increases the formation of lactic acid
which blocks urate secretion by the renal tubules.
Excessive alcohol consumption can have severe negative effects
in the ability of the kidneys to maintain the body's fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance.[7]
Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid or vitamin B3, has been used for many years to treat hyperlipidemia because it reduces total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) and triglycerides while it increases high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL). Elevated uric acid levels have occurred with niacin therapy, and the high dosages required for this treatment are associated with toxic side effects that include worsening of diabetes control and exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease and gout.[14]
A study of 46,393 men with no history of gout found that, during 12 years of follow-up, 755 eventually developed gout in direct proportion to the consumption of sugar-sweetened soft drinks.[16] The risk of gout was related to the amount of fructose consumed. Men who consumed two or more servings of sugary drinks per day had an 85% greater risk of developing gout. Fruit juices rich in fructose such as apple juice or orange juice were also associated with a higher risk of gout. Diet soft drinks were not associated with risk of gout.
Effect of Temperature and pH on Uric Acid Solubility
The solubility of monosodium urate is a function of temperature.
At normal body temperature, 37°C (98.6°F),
the maximum solubility of urate in physiologic saline is 6.8 mg per 100 ml,
but at 30°C (86°F) it is only 4.5 mg per 100 ml.[2]
Several studies have shown that gout attacks are more frequent in
springtime.[12, 13] This may be due to the accumulation of monosodium
urate crystals in the extremities during the cold winter months.
Some home treatments recommend applying ice or a
cold pack to the inflamed joint to help to reduce the pain and swelling,
but this may aggravate the problem because the low temperature
can cause additional uric acid to crystallize.
Uric acid also has higher solubility in solutions of alkali hydroxides and their carbonates than in acidic media. Acidity and alkalinity are measured using the pH (potential of Hydrogen) scale, which ranges from 0 for the most acidic solutions to 14 for the most alkaline solutions. The mid-point at pH 7 is neutral (neither acid, nor alkaline). In acid urine of pH less than 5.5, uric acid crystals precipitate and lead to stone formation. If the urine is neutral or alkaline, uric acid remains in solution and does not precipitate. At 37°C and pH 6.6, the solubility of uric acid is 6 mg per 100 ml, whereas at pH 7.0, uric acid is almost three times more soluble and forms stable solutions at concentrations of 16 mg per 100 ml.[15] Hydration with bicarbonate solutions has been effective in managing uric acid stones.[4]
Home Treatment for Gout
The elimination of uric acid from the body may be increased using a combined approach consisting of
|
Warming the joints may be accomplished with
a foot bath or a heating pad. Hydration requires increasing the volume of drinking water
to promote more frequent urination. The advice to drink eight glasses of water per day is based on the
general recommendation of the Institute of Medicine that men should consume roughly 3.0 liters
(about 13 cups) and women should consume 2.2 liters (about 9 cups)
of total water from all beverages and foods.
Alkalinization is accomplished by drinking a solution
of half a teaspoon of baking soda (sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO3) dissolved in a
glass of water.[5]
If you have a sodium restricted diet, this should be done under a doctor's supervision
since each half teaspoon of baking soda has 616 mg of sodium.
Sodium may be eliminated by using potassium bicarbonate instead of baking soda.
Potassium bicarbonate
is used to reduce the acidity of wines and may
be purchased through stores that sell winemaking supplies.
Baking soda is commonly used as a leavening agent for baking, but it is also a component of tooth pastes and it is frequently used as an antacid. Food grade sodium bicarbonate meets the requirements specified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a substance that is Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS). The dosage and directions for use as an antacid printed on the label of Arm & Hammer Baking Soda are:
The bicarbonate solution should be taken on an empty stomach, otherwise stomach acid (hydrochloric acid) will react with the bicarbonate to create salt (sodium chloride) and carbonic acid which breaks down into water and carbon dioxide gas. The carbon dioxide expands and increases internal stomach pressure that may cause injury if the stomach is overly full from food or drink. As a precaution, consult with a doctor or pharmacist if you are taking a prescription drug, since antacids may interact with certain prescription drugs. It is also advisable to use test strips to monitor the pH of the urine on a regular basis.
Concern about gout and cancer.
A study published in 2009 investigated whether uric acid, which has antioxidant properties,
could protect against cancer. The study found completely the opposite.
Gout patients had increased incidence of all types of cancer, including cancers of the oral cavity,
pharynx, colon, liver and biliary tract, pancreas, lung, skin (melanoma and nonmelanoma), endometrium
and kidney, as well as of malignant melanoma. The authors linked the occurrence of gout to increased
incidence of cancer and concluded that "hyperuricemia may be an early manifestation
of the carcinogenic process".[18]
Can cherries or tart cherry juice cure gout?
Cherries have been used in folk medicine to reduce inflammation, and cherry juice and various cherry extracts,
dried fruit, and juice concentrates have been promoted for treating or preventing gout and arthritis.
A research experiment conducted by the U.S. Department of Agriculture on 10 healthy women
showed that the concentration of plasma urate decreased, and that urinary urate increased
after eating 280 grams (slightly over half a pound) of Bing sweet cherries.[9]
However, there is not enough scientific evidence to support that cherries can cure gout. Since most episodes
of gout pain can subside without treatment, it is difficult to determine whether the relief
obtained with any therapy is due to the treatment or just coincidence.
On October 17, 2005 the FDA issued warning letters to 29 firms which claimed that cherry and other fruit-based products could cure diseases.[10] Some of the typical statements that the FDA targeted were:
"Cherry juice concentrate can be effective in reducing pain associated with gout."
"Cherry concentrate has been shown to help with the pain and swelling that is associated with arthritis and gout."
The FDA letters explain that these claims cause the products to be defined as drugs, and because these products are not generally recognized as safe and effective when used as labeled, they are also new drugs which may not be legally marketed in the United States without an approved New Drug Application requiring supporting scientific data.
Celery Seed and other herbal gout cures
Reputable medical sources are very vague about what a person should do to get relief from gout other than avoid eating
high purine foods, using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or obtaining medicines prescribed by a doctor.
The intense pain of gout makes people desperate and they are not satisfied with the relief provided by non-prescription
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen (Motrin), indomethacin (Indocin), ketoprofen (Orudis),
oxaprozin (Daypro), diclofenac (Voltaren), etodolac (Lodine), naproxen (Naprelan), and
sulindac (Clinoril).
Some people have found relief from gout pain by eating one tablespoon of celery seeds per day. Celery seed oil, a significant source of sedanolide, is used as a herbal remedy to treat inflammatory-associated conditions such as gout and rheumatism. As in the case of cherries, there is no conclusive scientific evidence that this treatment is effective. The Internet is full of advertisements that sell information about gout treatments or that promote supplements and herbs for which there is no scientific evidence of effectiveness. The herbal remedies include cherries, cherry extracts, cherry juice, celery seed, celery extract, cider vinegar, milk thistle, turmeric (curcumin), artichoke extract, garlic (Allium Sativum), Yucca Schidigera, and various Chinese herbs. There is little chance that cherries or any herbal products will be tested for effectiveness to satisfy the FDA requirements since pharmaceutical companies have no financial incentive to scientifically test cures using natural products for which they do not have exclusive marketing rights through patents or trademarks.
Alkaline Diet
The alkaline diet, also known as the alkaline ash diet, is based on the idea that different types of
food can have an effect on the pH balance of the body and decrease the risk of osteoporosis or other diseases
through increased alkaline ash production. Current scientific evidence does not support this hypothesis.[19]
The pH of the body is tightly regulated. Changes in the diet may affect the pH of the urine
because it is a waste product, they may not affect the pH of the blood.
In general, alkaline diets encourage the consumption of fruits and vegetables, but exclude grains, meat,
cheese, and eggs, which have important nutritional benefits.
Be skeptical when you evaluate home gout remedies advertised on the internet. Many of the products are expensive and not effective. You can search by typing your query in the search box. Typical results are listed below.
